Many people now rely on the internet, and slow WiFi connections can be annoying. A poor connection can be frustrating, whether you’re watching an episode of your favorite TV series or trying to submit a work mail.
Unlike light waves, WiFi can penetrate hard surfaces like doors and walls, which is why fluctuations in signal strength sometimes occur. A strong WiFi signal is necessary for seamless connectivity but can sometimes be challenging.
Factors That Affect Indoor WiFi Strength
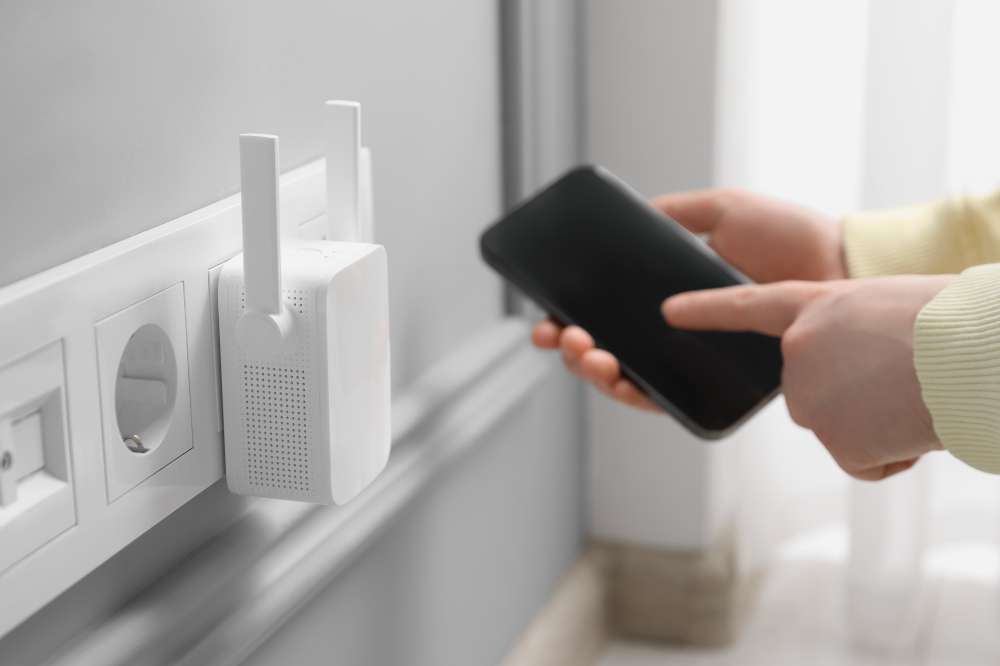

- Distance between router and connected devices: The more distance there is, the weaker the signal strength will be. This leads to slow data speeds and increased latency.
- Interference: Interference from other electronic devices, like cell phones, microwaves, and ovens, can affect signal strength. This especially occurs when these sources share the same frequency with the WiFi signal.
- Physical obstructions: Obstacles like large objects or walls can obstruct WiFi signals, reducing signal strength. Some objects have varying degrees of effects compared to others. For example, metals are more effective at blocking signals than wood. Dead zones frequently characterized by low or poor signal quality may also occur. They can be caused by large furniture and thick walls.
- Environmental factors: Temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions can affect the transmission and strength of WiFi signals.
Minimizing Interference
The following methods are quick ways to get rid of interference:
- Compatible with major cable internet providers including Xfinity, Spectrum, Cox and more. NOT compatible...
- [Compatibility] 12V Power Supply Adapter Compatible with Netgear, Linksys, Asus,Motorola, Motorola/Arris...
- Proper placement of the router. Place your router in an elevated or centralized position for better signal distribution.
- Adjust router settings: Try different channels to get the best signals with little or no congestion.
- The use of quality equipment: Outdated equipment is more prone to interference. Invest in high-quality routers and adapters, and upgrade outdated devices.
- WiFi extenders or mesh systems: Use these devices to identify and eliminate weak zones. This will help to avoid signal degradation.
There are different ways to fix weak WiFi connections, including internal ones. However, getting the best coverage can be difficult due to interference and signal loss. While there is no universal solution, the following suggestions can assist in improving the functionality of your wireless network.
10 Tips to Improve the Functionality of Your Wireless Network
Assessment
The first step to boosting the WiFi signal is to assess your current WiFi coverage. The assessment will help in observing your network’s performance. It will be easier to take note of and drop frustrating dead zones.
Using WiFi analyzer apps, you can check various rooms to identify weak and non-existent signals. These apps can provide the required information on signal strength, channel use, and potential sources of interference.
Router: Optimized Placement (Centralized and Elevated Position)
The strategic placement of your router can boost your WiFi signal strength. The closer your router is to the center of your coverage area, the better the reception you receive. It even helps distribute the signal in all directions.
A centralized placement also creates a closer attachment between your router and the connected devices. This strategy will enhance the signal’s strength and create balance and stability. An elevated placement can also enhance signal coverage. This will create a clear path for the signal to travel. Separation from nearby objects and mounting at high points will cut interference.
Router Hardware Upgrade
Compared to older standards, upgrading the hardware of your router provides a significant boost in the speed and capacity of your network. Before upgrading, check the qualities and usage patterns to know which suits you best. Consider the wireless standards and bandwidth capabilities.
Environmental Factors
Some environmental conditions may have negative effects. Adequate ventilation and maintenance of ideal interior environmental levels can enhance WiFi performance.
Hardware and Configuration
An increase in channel width can increase the data transfer rate, while an appropriate channel selection helps reduce interference.
In populated areas, many WiFi networks can overlap. Proper channel selection helps to avoid congestion and maximize signal quality.
Using the most recent security protocols helps to cut overhead related to authentication and encryption procedures. This provides appropriate security for your network.
Have a WiFi Password
If your WiFi does not have a password, do so right away. Too much connection to your network might lead to high consumption of your permitted bandwidth. This can slow down your connection speed.
Antenna Positioning and Direction
Most routers come equipped with either omnidirectional or directional antennas. Which one you use determines the focus of the signal strength.
Antennas can either be omnidirectional or directional. They are responsible for the transmission and receiving of signals.
Omnidirectional antennas can distribute signals in all directions, which results in low penetration of a particular space. The directional antennas offer a higher range by focusing signal strength in a specific direction.
The use of directional antennas is helpful in places with low signal transmission. They can be adjusted to focus on areas with weak coverage or away from interference sources.
Firmware Updates
This is a form of software optimization. The updates help to address bugs and vulnerabilities that may be present in the WiFi network.
There are two types of updates: manual and automatic. They introduce new features and enhancements. Many routers automatically download and install the latest firmware to reduce the possibility of forgetting important updates. Some users, however, prefer the manual updates to have more control.
DIY Methods
There are other cost-effective ways to boost your indoor WiFi signal. Handmade parabolic antennas, homemade extenders, and aluminum foil reflectors are some do-it-yourself (DIY) WiFi boosting techniques.
You can create a parabolic shape using cardboard or aluminum foil and attach it to your antenna. A spare router can be used to create WiFi range extenders, which can either be a repeater or an extender. Adjusting some router settings may also make a difference. These may include altering the WiFi channel or transmitting power.
These methods offer alternative techniques. They need little or no experience and allow you to enjoy reliable connectivity in your home.
When to Consider Hiring a Professional
DIY methods may not always be satisfactory. There are still instances where you may need the services of a professional. If you stay in a large or complex environment, you might need a professional to help set up custom solutions for a more general coverage.
In cases of persistent connectivity issues or wanting maximum wireless performance, seek a professional’s help.